math
- e3nn.math.orthonormalize()[source]
orthonomalize vectors
- Parameters
original (
torch.Tensor) – list of the original vectors \(x\)eps (float) – a small number
- Returns
final (
torch.Tensor) – list of orthonomalized vectors \(y\)matrix (
torch.Tensor) – the matrix \(A\) such that \(y = A x\)
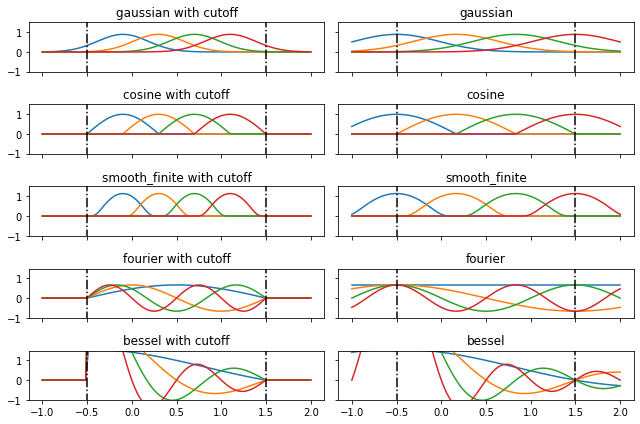
- e3nn.math.soft_one_hot_linspace(x: torch.Tensor, start, end, number, basis=None, cutoff=None)[source]
Projection on a basis of functions
Returns a set of \(\{y_i(x)\}_{i=1}^N\),
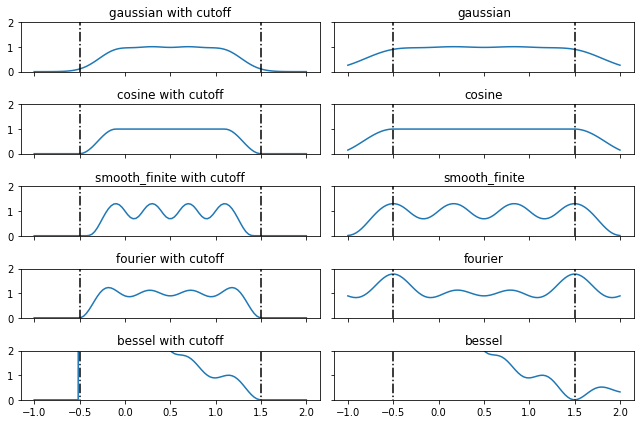
\[y_i(x) = \frac{1}{Z} f_i(x)\]where \(x\) is the input and \(f_i\) is the ith basis function. \(Z\) is a constant defined (if possible) such that,
\[\langle \sum_{i=1}^N y_i(x)^2 \rangle_x \approx 1\]See the last plot below. Note that
besselbasis cannot be normalized.- Parameters
x (
torch.Tensor) – tensor of shape \((...)\)start (float) – minimum value span by the basis
end (float) – maximum value span by the basis
number (int) – number of basis functions \(N\)
basis ({'gaussian', 'cosine', 'smooth_finite', 'fourier', 'bessel'}) – choice of basis family; note that due to the \(1/x\) term,
besselbasis does not satisfy the normalization of other basis choicescutoff (bool) – if
cutoff=Truethen for all \(x\) outside of the interval defined by(start, end), \(\forall i, \; f_i(x) \approx 0\)
- Returns
tensor of shape \((..., N)\)
- Return type
Examples
bases = ['gaussian', 'cosine', 'smooth_finite', 'fourier', 'bessel'] x = torch.linspace(-1.0, 2.0, 100)
fig, axss = plt.subplots(len(bases), 2, figsize=(9, 6), sharex=True, sharey=True) for axs, b in zip(axss, bases): for ax, c in zip(axs, [True, False]): plt.sca(ax) plt.plot(x, soft_one_hot_linspace(x, -0.5, 1.5, number=4, basis=b, cutoff=c)) plt.plot([-0.5]*2, [-2, 2], 'k-.') plt.plot([1.5]*2, [-2, 2], 'k-.') plt.title(f"{b}" + (" with cutoff" if c else "")) plt.ylim(-1, 1.5) plt.tight_layout()
fig, axss = plt.subplots(len(bases), 2, figsize=(9, 6), sharex=True, sharey=True) for axs, b in zip(axss, bases): for ax, c in zip(axs, [True, False]): plt.sca(ax) plt.plot(x, soft_one_hot_linspace(x, -0.5, 1.5, number=4, basis=b, cutoff=c).pow(2).sum(1)) plt.plot([-0.5]*2, [-2, 2], 'k-.') plt.plot([1.5]*2, [-2, 2], 'k-.') plt.title(f"{b}" + (" with cutoff" if c else "")) plt.ylim(0, 2) plt.tight_layout()
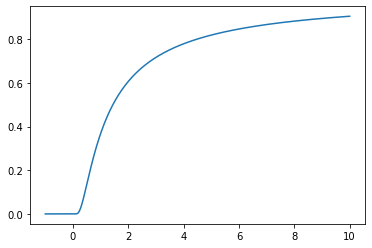
- e3nn.math.soft_unit_step(x)[source]
smooth \(C^\infty\) version of the unit step function
\[x \mapsto \theta(x) e^{-1/x}\]- Parameters
x (
torch.Tensor) – tensor of shape \((...)\)- Returns
tensor of shape \((...)\)
- Return type
Examples
x = torch.linspace(-1.0, 10.0, 1000) plt.plot(x, soft_unit_step(x));